Certinia is transforming traditional business processes in several industries. Certinia (FinancialForce) combines the Salesforce App Cloud’s power with an innovative cloud accounting system design. The result is a cost-effective solution that is way more than traditional bookkeeping & transaction processing, spawning a new generation of financial management products. Let’s discuss further about fundamentals of Certinia Accounting and how it is a game changer for your business.

Watch Our Webinar “FinancialForce ERP Basics and Accounting Basics” for a better understanding of Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting with Neeraj Garg, COO of AblyPro.
Top Reasons to Consider Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting ERP
Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting ERP is versatile solution enough to serve as an enterprise-wide accounting system, providing businesses with the ability to manage their finances & operations in a centralized location. It also has several features that allow businesses to track and analyze their financial data in many ways, making it easier to make informed decisions.
In addition, its ERP functionality allows businesses to automate many common business processes, saving time and money in the long run. There are several reasons to consider using Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting ERP, including:
- Flexibility: Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting ERP is highly flexible as well as customizable, allowing businesses of all sizes to customize the system to meet their specific needs.
- Efficiency: The modern ERP suite is fully automated & optimized for speed and efficiency, making it easy to manage business operations.
- Scalability: The functionality of Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting ERP can be expanded and upgraded as needed, allowing businesses to grow & evolve with the changing needs of their businesses.
- Security: Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting ERP incorporates advanced security features that protect your data from theft and other unauthorized access.
What is Accounting?
Accounting is the process of tracking and recording financial activity. Both individuals & businesses use the principles of accounting to assess their financial health and performance. It is considered as a vital part of any business, and the proper accounting will ensure that your business is capable of tracking its finances accurately and make informed decisions about future investments.
Key Terms of Accounting

1. Chart of Accounts
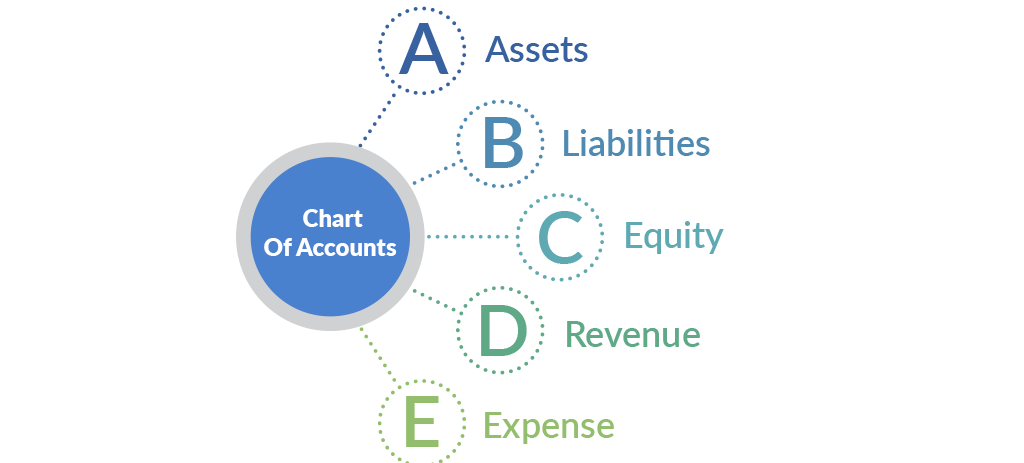
A chart of accounts (or COA) consists of a list of account names and numbers that appear at the beginning of your company’s financial record. It is considered as the starting point for entry into the accounting system and is critical to producing financial reports & set of rules that govern the application of standard accounting concepts & practices. It comprises of some major parts like assets, liabilities, revenue, expense, and equity (or capital).
2. Accounts Payable & Account Receivables
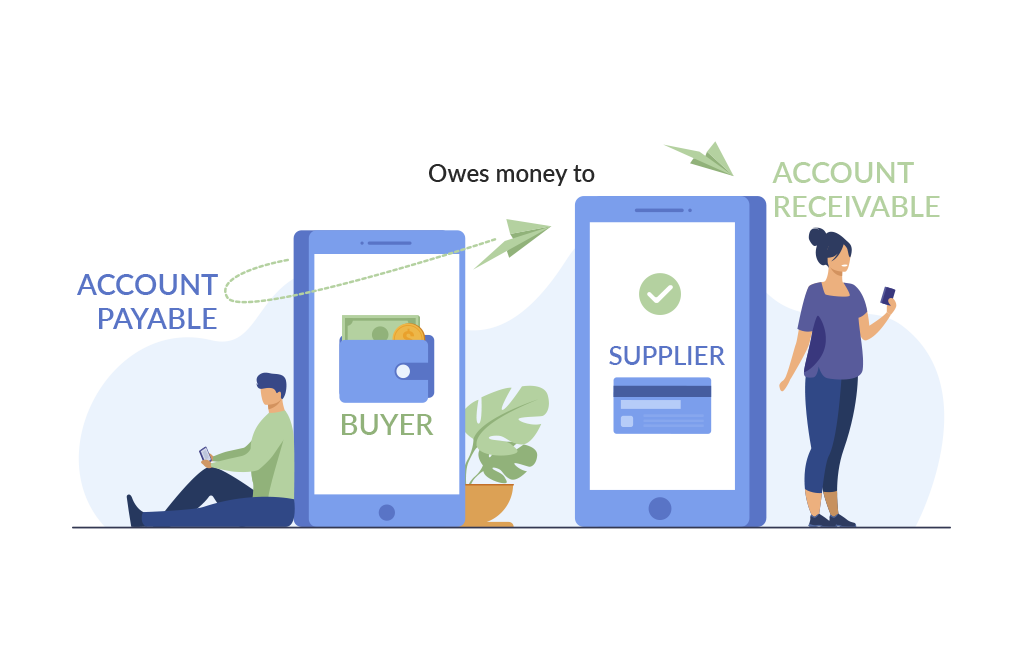
Generally, both Accounts Payable (A/P) and Accounts Receivable (A/R) are two important departments in any organization. The proper handling of these departments helps an organization maintain its financial stability.
Accounts Payable (or A/P) implies to all the bills that a company must pay on a monthly and yearly basis. These are usually paid on a 30-day or a 60-day cycle, depending on the bill. The function of AP is to manage these expenses promptly so that there are no issues paying bills on time.
Some examples of these include loan payments, utility payments (electricity, water, telephone, mobile), salary payments, insurance premiums, and vendor payments.
Accounts Receivables is paying invoices from vendors and suppliers. The Accounts Receivables process is sometimes referred to as A/R or A/P. Accounts Payable (A/P) and Accounts Receivables (A/R) are two different sides of the same coin but are handled by separate departments within a company.
3. General Ledger
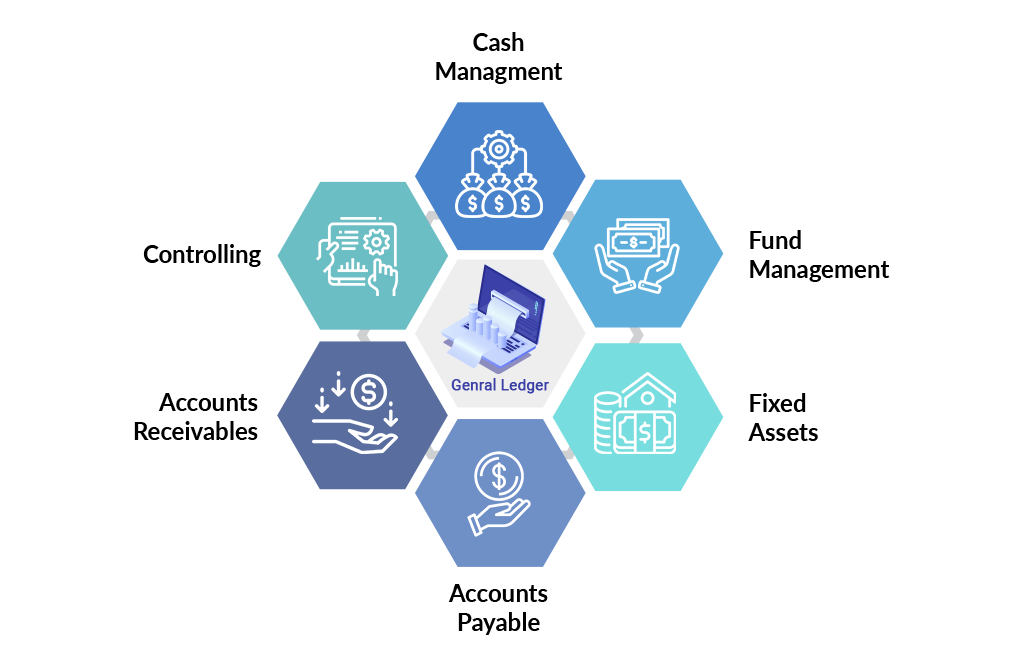
General Ledger is one of the two main types of financial records in accounting. It is a chronological record of transactions for all accounts from the beginning of the year to the end of the year totals. It has a basic purpose to ensure that all financial transactions are recorded and posted to prepare accurate financial statements. The general ledger must balance at the end of each accounting period. If not, adjustments must be made in the general ledger or subsidiary books or records.
4. Balance Sheet
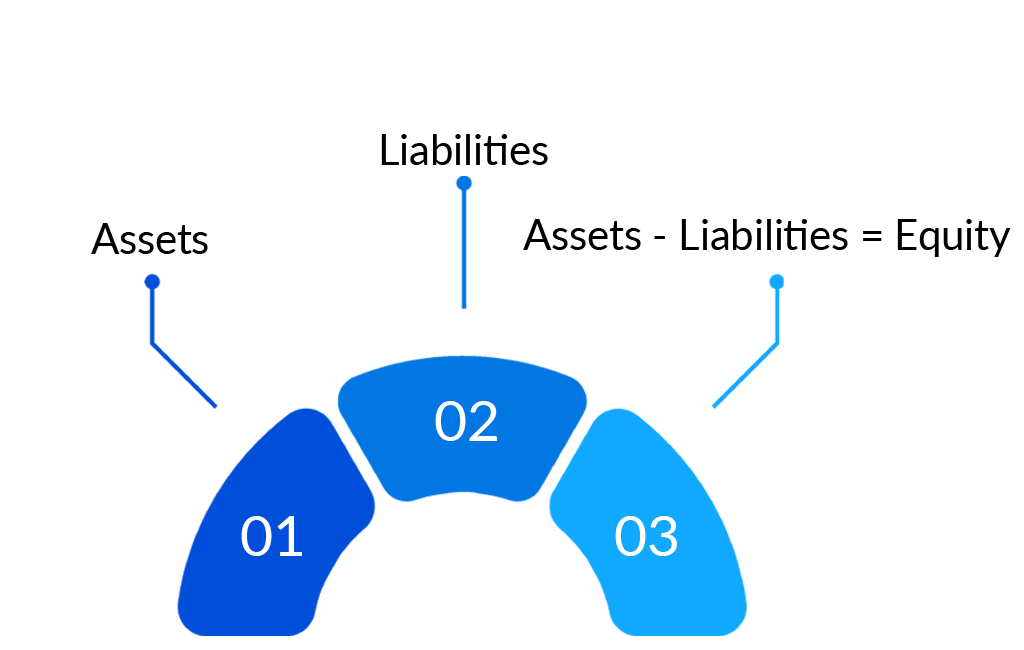
A balance sheet is a company’s report card; it summarizes a company’s or bank’s financial position at a given point in time. A balance sheet can be defined as a record of all a company’s assets, liabilities, and capital at a specific point in time, which is usually the end of the company’s financial year. It comprises three major parts, such as:
- Assets: These are the resources owned by the business. These can be anything from cash in the bank, and physical assets to intangible assets like goodwill. Assets are also organized into various categories, such as Fixed Assets and Current Assets based on their permanency.
- Liabilities: These are the debts and obligations of the company. These are primarily money borrowed from lenders but may also include other obligations such as rent payments, etc.
- Equity: The balance sheet shows assets minus liabilities, and hence is called Equities or net worth. It shows the worth (equity) of the company at a point in time in terms of assets and liabilities.
5. Income Statement Report
The income statement is a report that shows the company’s net income, cash flow from operations, total assets and liabilities for a specific period. The aim of such statements is to offer a detailed overview of the company’s performance over a specific period of time. It can also be useful for many purposes such as budget planning, cash flow analysis, risk assessment, diagnosing performance trends, and it goes on!
6. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement is another important document for businesses. It shows how much money the business has generated or spent each month, and where it came from (in terms of revenue and expenses). This information can help management decide where to allocate resources next. It also provides investors with information about a business’s cash flow (cash inflows minus cash outflows).
This document helps determine whether a company is a solvent and able to pay its debts as they come due. By understanding both reports, investors can make more informed decisions about where to invest their resources. You also gain useful insights into how profitable the business currently is and what changes are required to remain solvent in future years.
7. Trial Balance
A trial balance constitutes a bookkeeping worksheet in which all ledger balances are aggregated into equal debit and credit account column totals. A trial balance is prepared on a regular basis, usually at the end of each reporting period. It generally created to check the mathematical accuracy of the entries made in a company’s bookkeeping system.
8. Journal Entries
The journal entry reflects all transactions that took place in a business during one or more specified accounting periods. It includes information about the amount and type of asset, liability, equity instrument, or other monetary item involved in the transaction. Journal entries can reveal whether profits or losses were realized during the accounting period(s).
Journaling is another key element of preparing a successful financial plan, as it helps track your progress against your goals and adjust as needed. It can also assist you in identifying potential problems early on so that they can be addressed before they become larger issues.
How to Perform Basic Accounting Tasks in Certinia (FinancialForce)?
Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting is a robust financial accounting software that is simple to learn and implement, and easy to manage. Here’s a breakdown of what Certinia (FinancialForce) offers you in terms of carrying out basic functionalities in accounting management and additional features you can take advantage of.
Tasks Under General Ledger
- A multi-dimensional, flexible chart of accounts.
- Handling multi-currency and multi-company transactions.
- Transfer costs between firms or business units through inter-company transactions.
- Carry out accruals using automatic reversing journals.
- Calculation of cumulative, year-to-date budgets for each period is automatic.
- Get real-time visibility from the user and role-based dashboards.
- Access to financial report templates that are both standard and customizable.
Tasks – Accounts Payable
- Use document templates and electronic invoicing to reduce keystrokes.
- Utilize the authorization workflow for automated invoice and expenditure approvals.
- Establish vendor credit limits and credit terms for each vendor account.
- Pay vendors in cash or by cheque.
- Calculate due dates and settlement discounts automatically based on vendor terms.
- Avoid paying duplicate invoices.
- Create your own check printing formats.
Accounts Receivable
- With a simple click, create invoices from Salesforce opportunities.
- Set credit terms at the global and customer account levels.
- Calculate due dates and settlement discounts automatically.
- Calculate payments to invoices automatically based on document references and amounts.
- To chase down past-due accounts, use tasks as reminders.
- Chatter can be used to collaborate with sales and service workers.
- Send statements and letters of reminders through email.
- Use the “My Account” self-service billing interface or portal for customers.
- With the FinancialForce cash matching API, you can automate lockbox transaction processing.
Under Cash Management
- Cash flow and currency requirements are easily foreseen.
- Create multiple bank accounts in various currencies.
- Pay customer reimbursements from A/R (Accounts Receivables) to avoid duplicating records in A/P (Accounts Payable).
- Record one-time vendor payments and reimbursements to/from vendors.
- Reconcile your bank statements automatically without re-keying.
- Keep track of any bank charges and interest that appear on your bank statement.
Tasks Under Billing
- Create an invoice straight from any Salesforce CRM action (standard or custom objects).
- Generate a single invoice that includes numerous installment payment due dates.
- For regular bills, set up recurring invoices.
- Accounting entries can be generated for Certinia (FinancialForce) Accounting or your on-premise ERP system.

Key Takeaways
In case you are looking to increase the pace of your business with a robust ERP software, then you need Certinia Accounting. It is the way to go if you want to save time & money by removing departmental silos, multiple client data, and disconnected applications. Do you want to learn more about Certinia Accounting or implement it in your existing systems? Book a consultation.
Author

Project Manager, AblyPro
Manish Maid is a FinancialForce Project Manager at AblyPro with deep technical expertise in handling Enterprise Resource Planning software for optimizing Financial Management, Account Receivables, Account Payables, and other finance functions. With over 25 years of experience in training, implementation, business accounts and operations management, Manish enables organizations to simplify and streamline accounting complexities to optimize business processes while improving operational efficiency and boosting customer satisfaction.





